Figuring out how much to eat daily can feel overwhelming, but it’s a key part of a healthy lifestyle. Two essential concepts—Basal Metabolic Rate (BMR) and Total Daily Energy Expenditure (TDEE)—are the foundation for understanding your body’s unique caloric needs. In this guide, we break down what BMR and TDEE mean, the factors influencing them, and how to set personalised nutrition goals. With the right knowledge, you’ll be empowered to make smart dietary choices that support your fitness and wellness journey.
1. What is Basal Metabolic Rate (BMR)?
BMR Basics:
Your Basal Metabolic Rate (BMR) is the number of calories your body burns just to keep you alive at rest—think of it as the energy needed for essential functions like breathing and regulating body temperature. Even if you’re lounging on the couch, your body is working hard!
Factors That Impact BMR:
Several things affect your BMR, including age, gender, body composition, and genetics. Yes, you can thank (or blame) your DNA for a speedy or sluggish metabolism. Additionally, muscle mass boosts BMR, so building more muscle means burning more calories—even when you’re not moving.
How to calculate BMR:
To calculate your Basal Metabolic Rate (BMR) using the Harris-Benedict Formula, you’ll first need to know your weight, height, age, and gender.
The formula differs slightly for men and women.
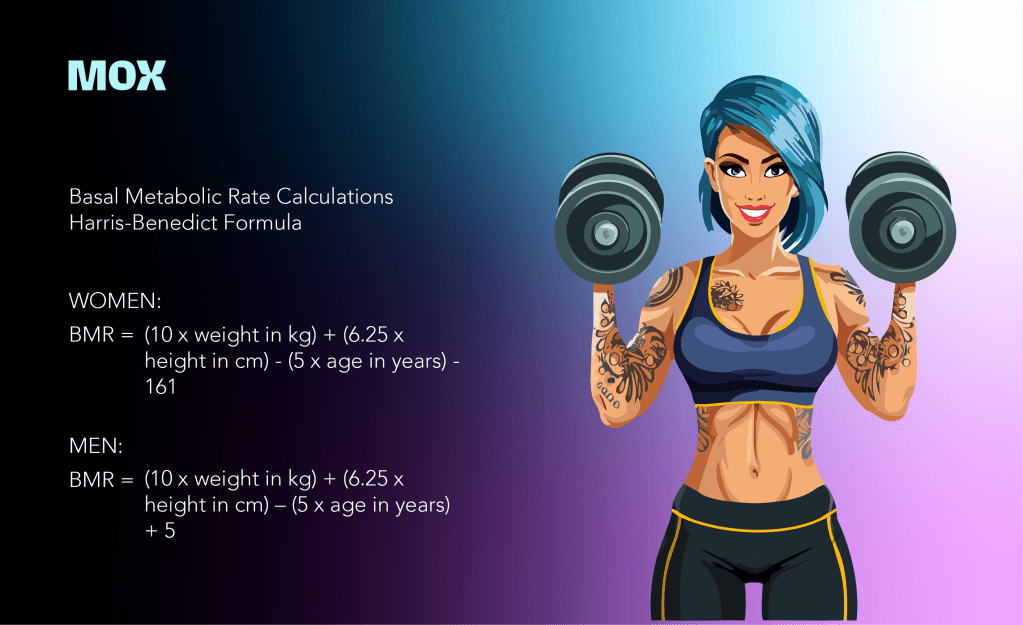
2. What is Total Daily Energy Expenditure (TDEE)?
TDEE Explained:
Your Total Daily Energy Expenditure (TDEE) includes your BMR plus the calories you burn through activities like exercising, walking, and even fidgeting. It’s the full picture of how much energy your body uses in a day.
How to Calculate TDEE:
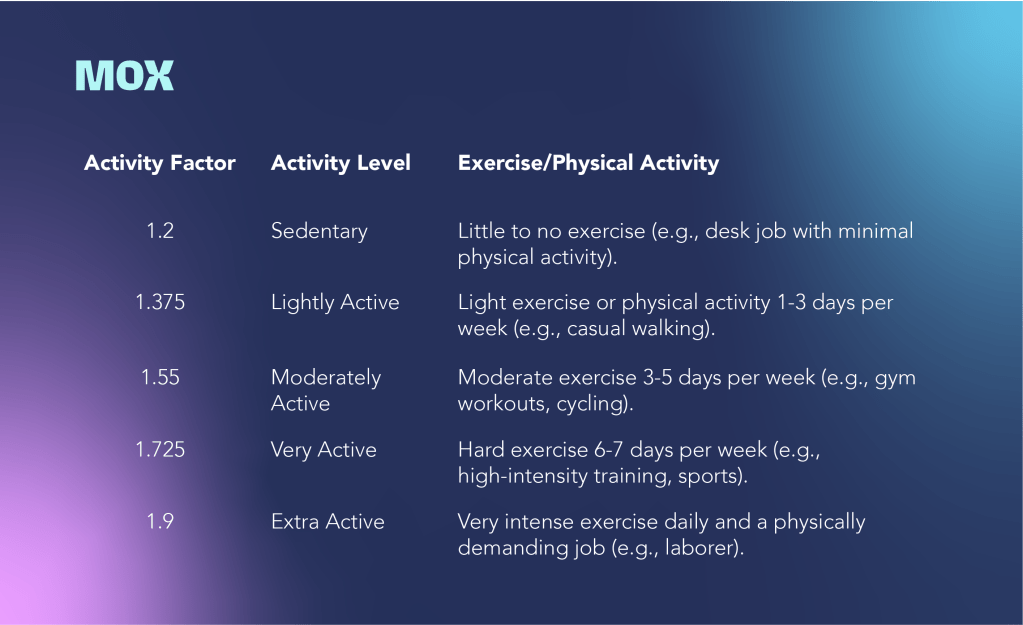
You can calculate TDEE using formulas like the Harris-Benedict Formula and multiply it by your activity factor, or rely on fitness trackers and online calculators for an estimate.
Let’s look at an example on how to calculate both BMR and TDEE:
A 30-year-old woman who weighs 70 kg, is 165 cm tall, and is moderately active (1.55 activity factor) would have a BMR of (10 x 70) + (6.25 x 165) – (5 x 30) – 161 = 1,420.25 calories.
To get her TDEE, she would multiply her BMR by her activity factor: 1,420 x 1.55 = 2,201 calories, meaning she needs approximately 2,201 calories per day to maintain her current weight.
3. What Influences Your Daily Caloric Needs?
Physical Activity Matters:
The more active you are, the more fuel your body needs. If you’re hitting the gym regularly, your body requires more energy to keep up. On the flip side, a more sedentary lifestyle means you won’t need as many calories.
Age & Gender:
Caloric needs naturally decrease as you age due to muscle loss and slower metabolism. Men typically have more muscle mass than women, which means they burn more calories overall. But with strength training, you can keep your metabolism humming no matter your age.
Metabolism & Muscle:
Since muscle burns more calories than fat, incorporating strength training into your routine can significantly increase your daily energy expenditure. Think of muscle as a calorie-burning powerhouse, even while you’re binge-watching Netflix.
4. How to Set Personalised Caloric Intake Goals
Aligning with Weight Goals:
To lose weight, you need to consume fewer calories than your TDEE. If gaining weight is your goal, you’ll need to eat more than your body burns. It’s all about creating the right balance between intake and expenditure.
Tailoring Intake for Health Objectives:
Whether you’re looking to enhance performance, manage a health condition, or simply boost energy, adjusting your caloric intake to your goals is key. Remember, food isn’t just fuel—it’s a tool for achieving your goals.
5. Balancing Macronutrients for Optimal Nutrition
Carbs, Proteins, and Fats—The Dynamic Trio:
Carbohydrates give you quick energy, proteins repair and build muscle, and fats help with hormone production and nutrient absorption. Balancing these macronutrients is crucial for keeping your energy steady and your body running smoothly.
Crafting a Balanced Diet:
When planning meals, aim for variety. Include a mix of lean proteins, complex carbs, and healthy fats to ensure you’re fueling your body with everything it needs. Think of your plate as a balanced, nutrient-packed work of art. Check out our blog on nutrition for women’s health and fitness to cover the basics!
6. Monitoring and Adjusting Your Diet
Track and Tweak:
Using food tracking apps or keeping a journal can help you stay on top of what you’re eating and how much energy you’re burning. Tracking allows you to adjust as needed—especially if you’re feeling fatigued or not seeing results.
Listen to Your Body:
Are you always hungry or overly full? These are signs your body might need more or less fuel. Adjust your caloric intake based on how you feel to avoid under or overeating.
7. Avoiding Common Myths and Pitfalls
Myth: Less is Always Better:
Cutting calories drastically isn’t always the best way to reach your goals. Quality matters! Focus on nutrient-dense foods that give your body the vitamins and minerals it needs, rather than just cutting numbers.
Common Mistakes:
It’s easy to miscalculate your daily needs, whether by overestimating your activity or underestimating how much you eat. The key is patience—fine-tuning your diet takes time, but you’ll find the sweet spot with consistency.
8. Seek Professional Guidance When Needed
Dietitians & Nutritionists:
If you’re unsure about your nutritional needs or dealing with specific health conditions, a professional can help create a customised plan. Nutritionists and dietitians are experts in helping you optimise your diet for your personal goals.
When to Consult a Doctor:
If you experience significant weight changes or health issues related to your diet, don’t hesitate to reach out to a healthcare provider. They can help you determine if you need to adjust your nutrition for long-term health.
Conclusion: Taking Control of Your Diet
Understanding your BMR and TDEE is the first step toward smarter eating. By knowing how much energy your body needs, you can set personalised goals that align with your health and fitness journey. Remember, it’s not just about how much you eat—but what you eat that counts. A well-balanced, nutrient-dense diet will help you stay energised, reach your goals, and maintain overall well-being.
